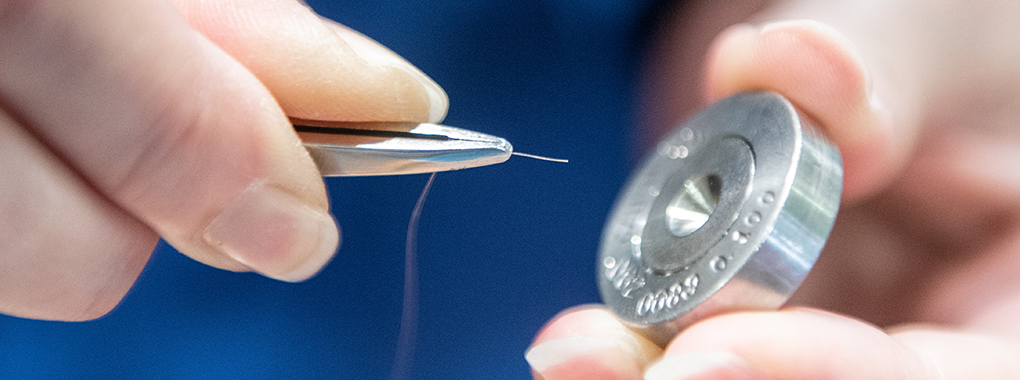
Technological InformationMore advanced

1. Plating (conductive)
Metals with good conductivity generally tend to have low strength. By coating these metals onto strong wire, it is possible to produce high-performance wire that offers both strength and conductivity.
For conductive plating, in addition to silver, copper and gold, all of which have excellent conductivity, we offer a lineup of Brass plating.
Along with carbon steel such as piano wire, non-ferrous spring materials such as phosphor bronze wire can also be used as the core.
By combining a variety of plating and core materials, we can provide wire with the advanced functionality that our customers require.
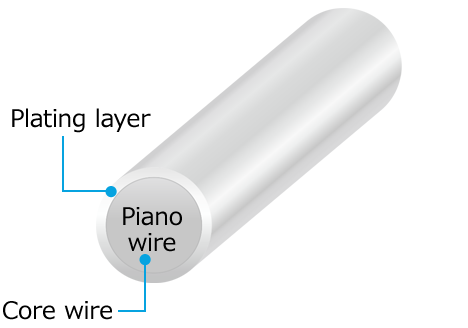 Silver plating
Silver plating
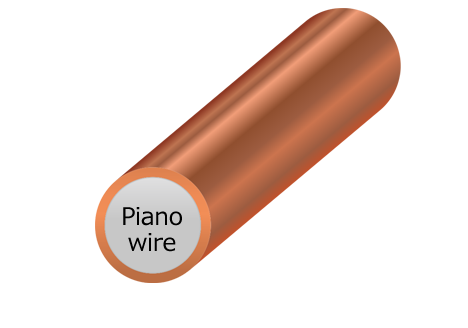 Copper plating
Copper plating
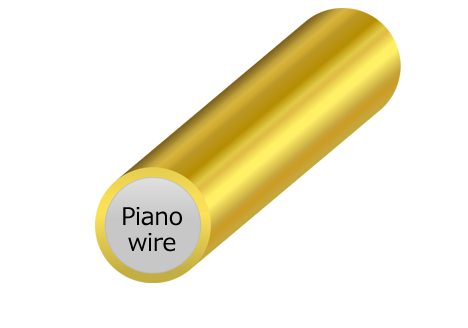 Gold plating
Gold plating
 Brass plating
Brass plating
 Silver plating
Silver plating
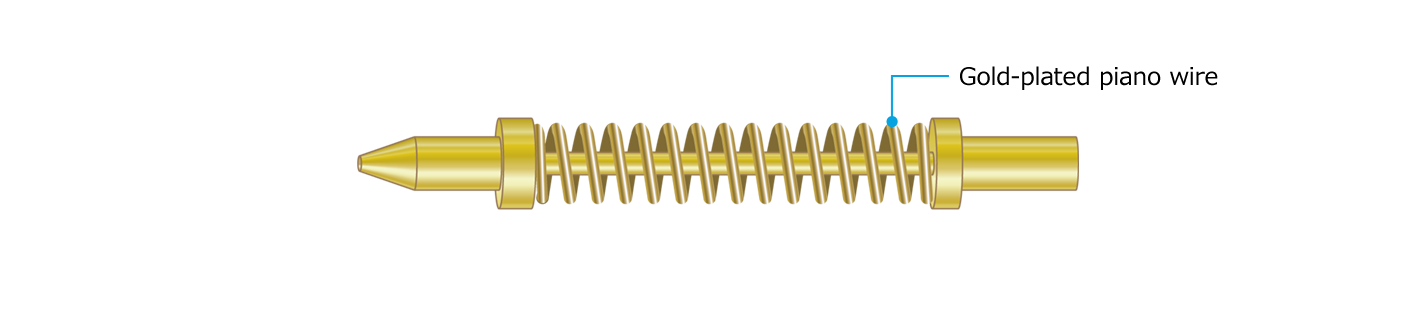 Application example: Springs for contact probe pins
Application example: Springs for contact probe pins
Conductive plating (wire cross-section for application example)
2. Plating (corrosion resistance)
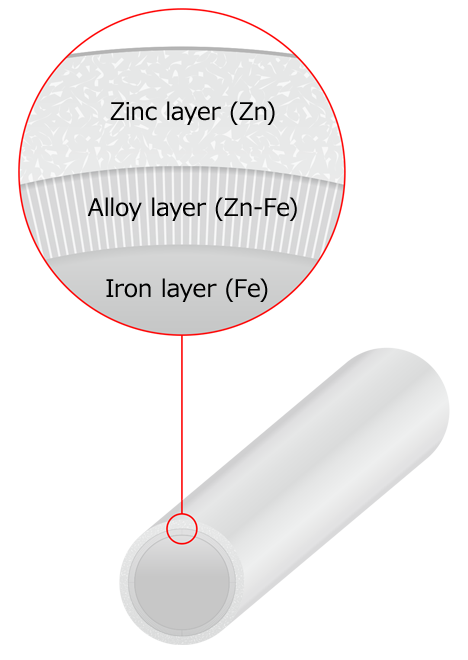
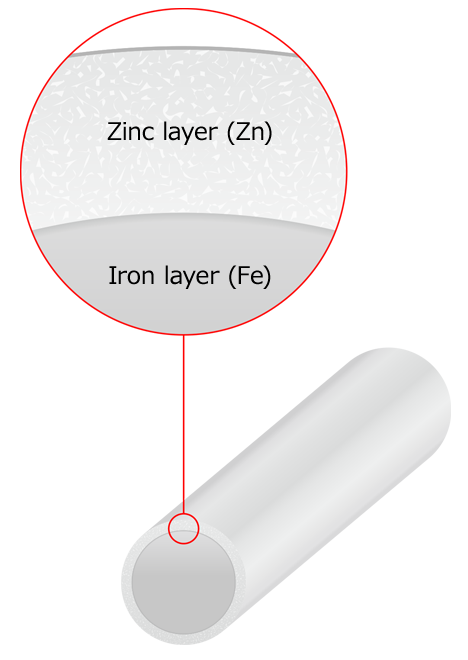
Sacrificial anticorrosion plating with metals such as zinc uses the ionization tendency of various metals to increase the corrosion resistance of steel.
Our galvanized wire is a corrosion-resistant plated wire utilizing zinc for sacrificial anticorrosion protection. Zinc plating can be achieved through hot-dip and electroplating methods. We use electroplating for small diameter wire and hot-dip plating for wire with a diameter of 0.70mm and above.
- *
- In hot-dip plating, an alloy layer is deposited at the interface with the wire substrate.
It is possible to achieve higher-performance wire by coating the wire with a metal that has a low ionization tendency to improve corrosion resistance. For carbon steel core wire, we can provide plating with nickel, tin and other anticorrosive materials.
 Galvanization
Galvanization
 Nickel plating
Nickel plating
 Tin plating
Tin plating
 Hot-dip galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing
 Electrogalvanization
Electrogalvanization
Corrosion resistant plating (wire cross-section showing plating layers)
3. Plating (other functional plating)
In addition to corrosion resistance, nickel plating offers excellent chemical resistance as well as characteristics such as resistance to atmospheric discoloration.
We utilize these characteristics for decorative purposes and other functionality, including tin plating for improved soldering performance.
4. Straightening
Straightening is the process of adding straightness to a wire that has a tendency to bend in the drawing process, through corrective processing or heat treatment.
By meeting straightness as well as other requirements, we provide a variety of high-performance wire products, including small-diameter wire for applications such as guide wire cores and medical devices, and large-diameter wire like our PC steel wire for structural components such as poles and pilings.
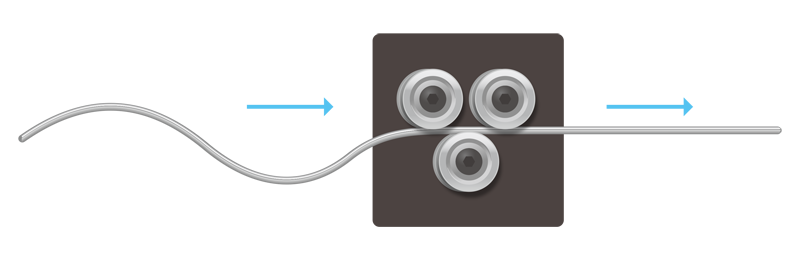
Straightening (processing example)